Understanding and Preventing Broken Heart Syndrome
Broken heart syndrome is real concern, especially for women over the age of 50, and the symptoms resemble a heart attack. How to protect yourself from this potentially deadly condition.
STORY AT-A-GLANCE
Negative emotions such as heartbreak, profound sadness and anger can lead to broken heart syndrome. The symptoms mimic a heart attack but without broken blood vessels
During broken heart syndrome your heart muscles are stunned and weakened, leading to your heart taking the shape of a balloon
The release of adrenaline during shocking and acutely stressful events, increasing blood pressure and pulse adds further strain to a weakened heart
With prolonged spousal illness also linked to mortality risk, it is extremely important to adopt a resilient and positive attitude when facing life’s challenges. A positive attitude has been shown to be the single most influential factor in longevity studies
It is impossible to avoid all negative experiences as too much of life is beyond our control. However, focusing on creating positive experiences and improving your health heart are two strategies that can help reduce the threat of broken heart syndrome
Broken heart syndrome is real, on the rise, and is a potentially deadly condition. Also called Takotsubo syndrome (TTS) or stress cardiomyopathy, more than 90% of cases are in women between the ages of 58 to 75. It is estimated that up to 5% of women suspected of having a heart attack actually suffered broken heart syndrome.1
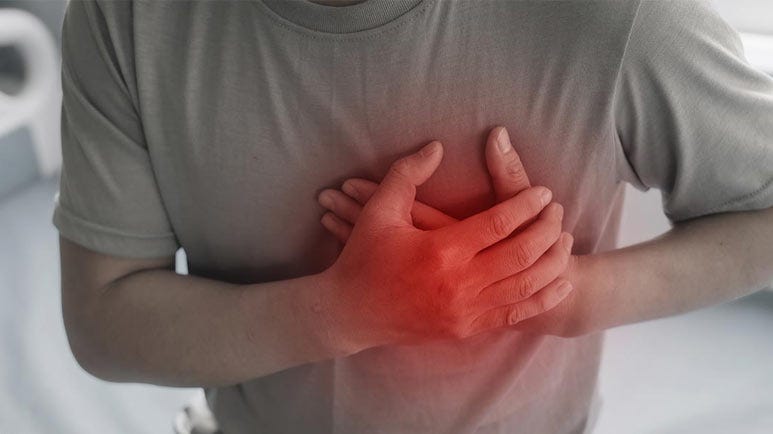
The symptoms mirror a heart attack. People who are experiencing broken heart syndrome describe sudden heart attack-like symptoms that include chest pain and difficulty breathing. The condition can last for a few days or even weeks, with the standard medications used to treat heart attacks often prescribed.2
While it is a relatively rare condition, it is estimated up to 2% of people who visit a health provider for a suspected heart attack actually suffered from TTS.3 Most recover fully but complications are possible and could be serious. Severe arterial blockages and clots can complicate matters, resulting in irreversible heart, congestive heart failure and even death.4 While cardiac function typically returns within a month, the mortality rate is as high as 8% according to a 2011 study.5
While it is impossible to avoid all negative events and stress, there are steps you can take to make yourself more emotionally and physically resilient to minimize your risk of broken heart syndrome.
Broken Heart Syndrome Versus the Widowhood Effect
TTS is often compared to the widowhood effect, which describes an increase in mortality rates shortly after a spouse dies. Studies have found excess mortality rates of 30% to 90% in the first three months after a spouse passes.6 The primary difference is that the cause of TTS has been narrowed down to the brain-heart connection, while the widowhood effect is not restricted to one aspect of human biology.7
A statistical analysis found that the death of a wife is associated with a 18% increase in all-cause mortality for men. The death of a husband resulted in an increase in mortality of 16% for women. In a notable parallel to TTS, a 7% to 10% increase of heart, vascular disease and heart failure death impacted the women covered in this study.
Previous seizures and strokes have also been linked to a higher incidence of broken heart syndrome.8 Chronic stress and depression are also linked with significantly increased odds of developing broken heart syndrome.9
Women Are at Greatest Risk
Women over 50 years of age are most at risk of broken heart syndrome. Overall, 85% to 95% of patients with TTS are women between 65 and 70. One study found that of 1,750 patients with TTS, the mean age was 67 and 89.8% were female.10
Cases of TTS have been on the uptick over the last two decades, with an especially pronounced increase among women aged 50 to 74. Some of this rise can be attribute in an overall increase in the size of this demographic but socioeconomic and environmental stressors may also play a role.11
Data on this increase in broken heart syndrome cases relies heavily on appropriate coding by the hospital. This is not a given when TTS presents so similarly to heart attack, including the focal point being the left ventricle. Despite the great potential for misdiagnosis, there is sufficient data to detect a steep increase in cases.12
Severe Stress Precipitates Broken Heart Syndrome
Events that have been known to trigger broken heart syndrome include the following.13 Seek medical attention right away if you suffer chest pains after a stressful event.
Car or other accident
Asthma attack
Serious illness, surgery or medical procedure
Death or serious illness or injury to a loved one, including a pet
Domestic violence
Financial loss
Intense fear
Public speaking
Sudden surprise
Job loss
Stress in general increases your risk of heart disease. Your body’s stress response is supposed to protect you but constant stress takes a serious toll on your health. The hormone cortisol is released in response to stress, and chronically elevated cortisol levels promotes high blood pressure and inflammation, both of which contribute to heart disease.
Cortisol is also catabolic, meaning it breaks down your muscle tissue, and antimetabolic, meaning it lowers your metabolism. It promotes fat storage around your internal organs and inhibits collagen formation.
How to Protect Yourself From Broken Heart Syndrome
It is not possible or realistic to attempt to evade all stressful life events. Instead, the best approach is to develop strategies to manage stress and escape the stress cycle. This can help minimize the release and impact of stress hormones14 and improve your resilience. Here are several suggestions:
Minimize exposure to fear narratives — With endless access to screentime and content, it is easy to “doom scroll” through a never-ending wave of infuriating and depressing news. Constantly seeking and fixating on stressful events outside of your control can be accomplished with a swipe or a click.
The average adult spends more time staring at a screen than sleeping. Putting down your screen not only can not only help you break this cycle of stress but is an important step towards getting more and better-quality sleep.15
The narratives spun in our own heads can be as powerful as the false narratives spun by the media. Changing the narrative is a powerful way to increase resilience and end the rumination cycle. Rumination describes the process of reliving bad events in your head over and over.16
Emotional Freedom Techniques (EFT) — Also referred to as tapping, EFT is one my favorite tools to reduce stress and increase creative problem solving. Using the same meridians as acupuncture, EFT instead stimulates these pathways with tapping while voicing positive affirmations. EFT has a range of benefits, both physical and mental.
Expressive writing — Another powerful tool is expressive writing. This practice involves free writing for 20 minutes about an issue, exploring your thoughts and feelings about it. A 1988 study found that expressive writing provides a sense of control that reduces stress. Participants who wrote four times per week were healthier in six weeks and happier three months later than those who wrote about superficial topics.17
Meditation — Avoiding stressful situations may be the first line of defense against broken heart syndrome but meditation has proven helpful to some patients with TTS.18 Journaling mindfulness, yoga or even relaxing activities like a bath have also been shown to reduce break the stress cycle and protect your heart.19
Spend more time outdoors — There is compelling evidence that outdoor walks, outdoor exercise, nature walks, and nature viewing contribute to improved heart rate and blood pressure. Spending 120 minutes outdoors per week can improve your health and well-being by reducing stress.20 Depression and anxiety are linked to broken heart syndrome. A simple walk in green and natural spaces can reduce anxiety and boost your mood.21
Gardening — A form of exercise and a popular hobby, gardening can reduce stress and serve as a sleep boosting exercise.22 A study during the first wave of COVID-19 related lockdowns found that gardening helped foster a connection with nature, relieve stress, provide an outlet for exercise and a source of healthy nutrients.23
Slow breathing through your nose — If you are looking to improve oxygenation and bust stress, breathing through your nose is a practice worth mastering. A study to measure the effect of slow nostril breathing found that twelve weeks of slow breathing exercise reduced perceived stress and improved cardiovascular parameters.24
Protect your heart with better sleep — Chronic sleep deprivation leads to higher levels of stress hormones like cortisol and affect appetite regulating hormones like leptin and ghrelin.25 Cortisol contributes to cardiovascular disease.26
Magnesium and B6 — The combination of magnesium and B6 can have a complementary effect that reduces stress. Especially when compared to adults with low magnesium levels.27 Magnesium is also effective for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.28 In industrialized western countries, magnesium deficiencies in the diet increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and death.29
Building Resilience Is the Best Protection Against Broken Heart Syndrome
Pursuing a lifestyle that enhances and protects your heart health can serve to protect you from the worst effects of TTS. Broken heart syndrome can improve very rapidly if treated on time and identified accurately by a doctor familiar with the syndrome. The good news is that recurrence is fairly uncommon, and as long as the heart muscle is not damaged, most people who suffer broken heart syndrome continue to lead healthy lives.30
A healthy heart is better able to endure the rapid weakening of the heart muscle that occurs in broken heart syndrome. Reducing stress and using tools that protect you from being overwhelmed by stress can protect your heart from stress damage. These tools may also make you more emotionally resilient in the face of serious challenges and less likely to suffer broken heart syndrome.31
Disclaimer: The entire contents of this website are based upon the opinions of Dr. Mercola, unless otherwise noted. Individual articles are based upon the opinions of the respective author, who retains copyright as marked.
The information on this website is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice. It is intended as a sharing of knowledge and information from the research and experience of Dr. Mercola and his community. Dr. Mercola encourages you to make your own health care decisions based upon your research and in partnership with a qualified health care professional. The subscription fee being requested is for access to the articles and information posted on this site, and is not being paid for any individual medical advice.
If you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication, or have a medical condition, consult your health care professional before using products based on this content.




Cardiovascular diseases rank first among the diseases that cause the most deaths in the world, responsible for 40.6% of total deaths in the world.
Dr. Mark, who emphasized the need to build on the seven pillars of health, namely nutrition, sleep, stress management, movement, genetics, hormones avoiding metabolic diseases.
Dr. Mark, who has a full-time wellness-based medical practice in Tulsa, Oklahoma, along with his wife, Dr. Michele, said stress is one of humanity's most obvious killers right now and many don't understand the idea of being stressed.
“Many people end up with hypertension. Sometimes they end up with high blood sugar which can eventually result in low blood sugar due to a sort of adrenal gland shock. The adrenal glands simply can't keep up. So stress is hugely important today,” said Dr. Mark, adding that it is important to define stress appropriately and recognize what the inappropriate definition of stress is.
Multiple reports appear to support the belief that acute psychological stress can precipitate myocardial dysfunction, infarction, arrhythmia, and cardiac death. Activation of cardiac sympathetic outflow and inhibition of cardiac vagal are important mediating mechanisms. Acute stress causes a high amount of catecholamines to be secreted into the blood. These hormones can cause many changes in the body, such as tachycardia, high blood pressure, coronary vasoconstriction, and/or stress cardiomyopathy. Chronic psychological stress is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. With an increase in the level of anxiety, there is a change in the activity of the sympathetic-adrenal, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone systems. Furthermore, it is naturally accompanied by changes in carbohydrate, protein and lipid metabolism, procoagulant changes in hemostasis and impairment of vascular endothelial function. All these disorders can lead to increased progression of atherosclerosis, increased coronary vascular tone, increased instability of atherosclerotic plaques, tendency to thrombosis and contribute to the aggravation of the course of coronary heart disease. When we experience constant stress, our amygdala sends signals to the bone marrow to produce more white blood cells, which causes leukocytosis. This in turn causes the arteries to become inflamed and can cause some cardiovascular problems and others as I mentioned before: Heart attacks, angina and stroke.
Also, a team of scientists from McMaster University in Ontario (Canada) has studied the link between the use of antidepressants and the risk of mortality, through a meta-analysis of existing research from several medical databases, looking for a link between mortality and the use of antidepressants. The analysis included 16 studies, with approximately 375,000 participants.
They extracted data on cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular risk and the type of antidepressants taken. They then used a mixed-effects model to conduct their meta-analysis, controlling for depression and other illnesses.
The results revealed that, in the general population, people who took antidepressants had a 33% higher risk of dying prematurely than people who did not take these drugs. Additionally, antidepressant users were 14% more likely to have an adverse cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack.
https://www.brighteon.com/506133ec-febd-4afc-98cb-493b04011917 .---
https://www.ctvnews.ca/health/antidepressant-use-linked-to-higher-risk-of-premature-death-study-1.3594717?cache=yesclipId104062%3FclipId%3D68597 .---
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319462 .----
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002934322001371 (2022).---
https://peerianjournal.com/index.php/tpj/article/view/324 (2022).----
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1566070221001557.(2022)
https://www.opastpublishers.com/open-access-articles/the-role-of-stress-in-the-development-of-cardiovascular-diseases.pdf (2023)